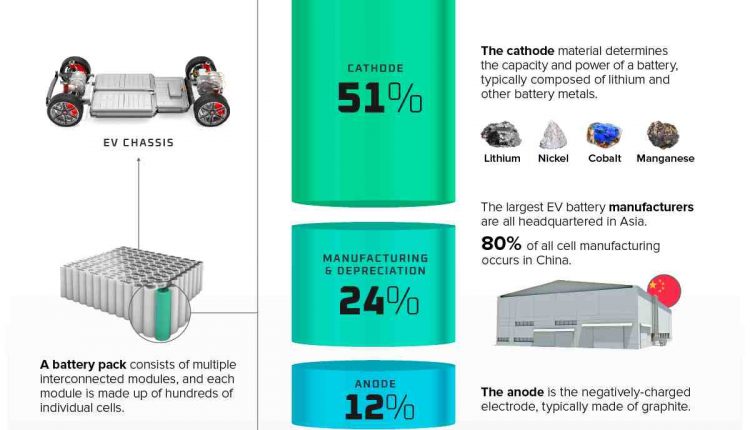
Rechargeable lithium ion batteries are used to power many electronic devices in our daily lives, from laptops and cell phones to electric cars. Lithium ion batteries on the market today are usually based on a liquid solution, called an electrolyte, in the center of the cell.
When a battery is powered, lithium ions move from the negatively charged end, or anode, through the electrolyte, to the positively charged end, or cathode. When a battery is charged, ions flow in the opposite direction from the cathode, through the electrode, to the anode.
Water-based lithium ion batteries have a major safety issue: they can catch fire when overcharged or short-circuited. A safer alternative to liquid electrolytes is to build a battery that uses a solid electrolyte to transport lithium ions between the anode and cathode.
However, previous research has found that a strong electrolyte causes tiny metal particles, called dendrites, to form on the anode as the battery charges. These dendrites short circuit batteries at low currents, making them useless.
Dendrite growth begins with small defects in the electrolyte at the boundary between the electrolyte and the anode. Scientists in India recently discovered a way to slow dendrite growth. By adding a thin layer of metal between the electrolyte and the anode, they can stop the dendrites from growing into the anode.
The scientists chose to study aluminum and tungsten as possible metals to build this thin metal. This is because aluminum or tungsten mix, or alloy, with lithium. Scientists believe that this will reduce the possibility of defects in lithium. If the selected metal contains lithium, a small amount of lithium can move into the metal layer over time. This will leave a type of defect called a negative in the lithium where a dendrite can form.
In order to test the quality of the metal layer, three types of batteries were assembled: one with a thin layer of aluminum between the lithium anode and the electrolyte, one with a thin layer of tungsten, and one with no metal.
Before testing the batteries, the scientists used a powerful microscope, called a scanning electron microscope, to take a closer look at the boundary between the anode and the electrolyte. They saw small pits and holes in the sample without any metal, noting that these defects can be places for dendrites to grow. Both batteries with aluminum and tungsten layers look smooth and continuous.
In the first test, the current was cycled continuously through each battery for 24 hours. The battery without a small metal short-circuited and failed within the first 9 hours, probably due to dendrite growth. Neither aluminum nor tungsten battery failed in this first test.
In order to know which type of metal is better to stop dendrite growth, an experiment was done on only the sample of aluminum and tungsten layer. In this test, the batteries are cycled by increasing the amount of current, starting from the current used in the previous test and increasing by a small amount at each step.
It is believed that the current density with which the battery circulates is the most important current density for dendrite growth. A battery with an aluminum layer fails three times the starting current, and a tungsten battery fails more than five times the starting time. This test shows that tungsten is better than aluminum.
In addition, the scientists used an electronic microscope to look at the boundary between the anode and the electrolyte. They found that voids began to form in the metal at two-thirds of the critical mass measured in the previous experiment. However, it is empty within one-third of the current value. This confirms that void formation continues with dendrite growth.
The scientists then ran calculations to understand how lithium interacts with these metals, using what we know about how tungsten and aluminum react to changes in energy and temperature. They showed that aluminum layers have a high potential to develop corrosion when in contact with lithium. Using these calculations will make it easier to choose a metal type to try in the future.
This research shows that solid state batteries are safer when a thin layer of metal is added between the electrolyte and the anode. The experts also show that choosing one metal over another, in this case tungsten instead of aluminum, can make batteries last even longer. Improving the performance of these types of batteries will bring them one step closer to replacing the highly flammable liquid batteries on the market today.
TOKYO — Toyota Motor is the leading holder of state-owned battery properties, a Nikkei survey shows, showing how Japanese companies are dominating the race to develop the future power source for electric vehicles.
Contents
What will replace lithium batteries in the future?
The solution could be a sodium-ion battery. Sodium-ion technology consumes very little natural resources – and its production does not require hard lithium salt – simple table salt is enough. However, sodium is three times heavier than lithium, which means sodium-ion batteries are also heavier.
What battery technology will replace lithium-ion? Dual carbon Perhaps the front-runner in the race to replace lithium-ion, this technology uses carbon in both the anode and cathode of the battery, providing a capacity comparable to lithium-ion but at a longer working life with improved efficiency safe and relatively cheap. tool.
What is the most promising new battery technology?
5 New Battery Technologies That Will Change The Future
- NanoBolt lithium tungsten battery. Working on battery anode materials, researchers at N1 Technologies, Inc. …
- Zinc-manganese oxide battery. …
- Organosilicon electrolyte battery. …
- Gold nanowire gel electrolyte battery. …
- TankTwo String Cell⢠battery.
What is Elon Musk’s new battery?
Tesla has been using LFP in some of its entry-level, 3-model models in the United States since last year, expanding the use of the technology beyond China, where about two years ago it started using LFP batteries with CATL. made by China (300750). SZ), the world’s largest EV battery maker, for some Model 3s.
What is the latest breakthrough in battery technology?
A research team from the US Department of Energy’s Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (PNNL) has developed a sodium-ion battery with extended life.
What is the battery that could change the world?
In short, lithium-sulfur batteries can enable multiple functions to use electricity, which will make zero emissions easy. Surprisingly, it gets even better. Lithium, sulfur, and other materials that make this new battery are abundant in the world.
Is there anything better than lithium-ion batteries?
Fluoride batteries have a potential to last eight times longer than lithium batteries, but that is easier said than done. This is because fluoride is an anion, or negatively charged ion, which is the magic behind its high energy content but also the reason why it is active and difficult to balance.
What will replace lithium-ion batteries?
Salt. Salt, or sodium, is a close chemical cousin to lithium. While the species i type type type type type type type type type type type type type type type type type type type type type type type type type type type type type type type (i) of the environment, meaning it can be a viable option to replace it. The solution could be a sodium-ion battery.
Which can be the best alternative to lithium-ion batteries in future?
One of the best alternatives is to use sodium-ion (Na-ion) batteries over lithium-ion batteries. Na-ion batteries have several advantages over conventional Li-ion batteries in a variety of end-use applications. Lithium and sodium are both alkali metals, and are next to each other on the periodic table.
What is the Holy Grail of batteries?
Drexel University scientists have found a way to improve the performance of lithium-sulfur batteries for EVs. These powerful cells, considered the “holy grail” of batteries, are said to be superior to regular Li-ion batteries due to their stability and structure.
Will there be an alternative to lithium?
Researchers have discovered an alternative to lithium-based battery technology by developing sodium glass electrodes that are capable of supporting long-term, balanced energy storage.
What will replace lithium in the future?
Magnesium. Magnesium is currently being researched as an active ingredient in future batteries. It is an element that can hold a charge of 2, which is greater than both lithium and sodium.
Is there anything better than lithium?
Fluoride. Fluoride batteries have a potential to last eight times longer than lithium batteries, but that is easier said than done. This is because fluoride is an anion, or negatively charged ion, which is the magic behind its high energy content but also the reason why it is active and difficult to balance.
How do I know if my lithium ion battery is safe?
There are 5 warning signs that your lithium battery is damaged:
- Work force is reduced.
- The electricity is low.
- The output is high.
- The battery is overheating.
- The battery is swollen.
Are old lithium-ion batteries safe? Are Lithium-Ion Batteries Really Dangerous? Indeed! Lithium-ion batteries are definitely waste. After the battery is no longer used because it seems it will no longer hold a charge, it is time to get rid of it.
How can I tell if my lithium battery is healthy?
Remove the battery and put a voltmeter on it and put the voltage you got and put the battery in it. If the battery is dead or at the end of life, then it will no longer hold a charge. If the battery is dead or at the end of life, the battery will be slightly swollen.
What kills a lithium battery?
Heat is the leading cause of death for lithium batteries. High temperature or low temperature can kill the lithium battery. The result of a decrease in temperature is a decrease in the change of active chemicals in the cell.
At what voltage is a lithium ion battery dead?
The voltage starts at a maximum of 4.2 and quickly drops to about 3.7V for most of the battery life. Once you hit 3.4V the battery dies and at 3.0V the circuit breaker disconnects the battery (more on that later.
How do you test a lithium battery with a multimeter?
What can ruin a lithium battery?
Cracks or cracks can allow moisture and oxygen to enter the battery and corrode the lithium contents, causing overheating. This may cause a fire or explosion. Overheating, overcharging and shock from falling or crushing can also cause heat reactions.
What can cause a lithium battery to explode?
The chemicals inside the battery begin to heat up, which causes further damage to the device. Eventually the battery could hit temperatures above 1,000F. At this point the electricity can ignite or even explode when exposed to oxygen.
What can damage a lithium battery?
Physical impacts that can damage lithium batteries include dropping, crushing, and punctures. Damage to all types of lithium batteries can occur when temperatures are high (eg, above 130°F). External heat sources (eg, open fires, heaters, etc.)
How much does a graphene battery cost?
In simple terms, a graphene battery can have a higher capacity compared to a lithium-ion battery in the same physical size. It is worth saying that although graphene seems to be ready for the market, there is more than meets the eye. Graphene is not cheap, as one sheet can cost $25.
How good is a graphene battery? Graphene offers superior electrical properties than lithium-ion batteries. This allows for fast charging cells that are capable of delivering very high currents as well. This is especially useful for powerful car batteries, for example, or fast charger to charger.
How far away are we from graphene batteries?
Graphene lithium-ion battery This technology is only 1-2 years old but requires investment in graphene production.
Does Tesla use graphene batteries?
What is the problem with graphene batteries?
There is a big problem though: Although scientists have demonstrated graphene-based batteries with performance characteristics that exceed those available commercially, the lack of techniques that can be used to mass produce high-quality graphene is limit their potential for practical use, for example in …
Are graphene batteries the future?
Graphene batteries haven’t been able to power phones and other devices yet, although Samsung is rumored to have something in the works. In the future, graphene could be the material that replaces the lithium-ion batteries that the tech industry has relied on for years.
How fast do graphene batteries charge?
Yes, graphene, that miracle material that has long promised to change the world, allows this 10,000mAh battery to charge from zero to full in less than 30 minutes, about five to six times faster more than a conventional power bank.
What is the problem with graphene batteries?
There is a big problem though: Although scientists have demonstrated graphene-based batteries with performance characteristics that exceed those available commercially, the lack of techniques that can be used to mass produce high-quality graphene is limit their potential for practical use, for example in …
Do graphene batteries need a special charger?
The so called graphene batteries are Lipo batteries so yes, they can be safely charged by a Lipo charger. Try the China Hobby line, Pulse, or the new Tatu packs, or Dinogy, they work well. Turnigy batteries are old stuff, there are better things out there now.
How long does graphene battery last?
Among the types of graphene-based battery technology, graphene lithium-ion batteries are expected to be implemented in the next 1-3 years, solid-state batteries in the next 4-8 years, and graphene supercapacitors in 10 years.
Are graphene batteries available?
Although the use of graphene batteries in EVs is currently possible, they have not yet been commercially available as more research is needed to develop more production techniques and further assess the material’s efficiency. Several companies have shown interest in graphene batteries to power EVs.
Do graphene batteries exist?
Graphene-based batteries are quickly becoming more convenient than their graphite predecessors. Graphene batteries are an emerging technology that allows for increased electron density, faster cycle times, and the ability to hold a charge longer thus improving battery life.
How soon will graphene batteries be available?
Current manufacturing equipment and processes currently used to manufacture lithium-ion bag and cylinder batteries can produce graphene batteries for Nanotech Energy, and a factory designed to build them in the current state now scheduled to open in late 2022.
How much does graphene battery cost?
Black Graphene Grade : Battery / Supercapacitor, Rs 18000/kg | ID: 20827933173.
At what temperature do Li ion batteries start becoming a danger?
Never store batteries in temperatures above 170°F (76°C) as this may cause burns.
What is the wrong temperature for batteries? Battery life decreases at higher temperatures Battery life decreases at higher temperatures â every 15 degrees F above 77, battery life is cut in half. This is true for ANY type of lead-acid battery, whether sealed, Gel, AGM, industrial or otherwise.
What temperature is bad for lithium-ion batteries?
Generally, lithium-ion batteries can be charged in temperatures up to 113°F and discharged in temperatures as high as 140°F.
Is it bad to leave lithium batteries in the cold?
Now, researchers at the Department of Energy’s SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory have discovered another overlooked part of the problem: Storing lithium-ion batteries at temperatures below freezing can crack parts of the battery and separate them from the material. around, reduces the power storage capacity. …
At what temperature do lithium-ion batteries get damaged?
At temperatures above 60°C the Li-ion battery regularly loses capacity and therefore efficiency.
How cold is too cold for lithium-ion batteries?
When the temperature of your battery falls below 32 degrees, the lithium cells cannot receive the same amount of charge current (warm) as they did when the temperature is hot. Do not charge your lithium battery when the battery temperature is below freezing.
How hot can lithium batteries get before they explode?
Eventually the battery could hit temperatures above 1,000F. At this point the electricity can ignite or even explode when exposed to oxygen. Will these catastrophic failures, unlikely though they may be, spell the end of the Li-ion battery? Impossible, said Buchmann.
Can lithium batteries explode if they get too hot?
Lithium batteries have become popular since they can deliver three times more power than other battery technologies. Lithium-ion batteries are also completely rechargeable. However, lithium batteries also have some disadvantages. They can get very hot, which can cause explosion and fire.
Is it common for lithium batteries to explode?
Fortunately, major explosions caused by Li-ion batteries are rare. If they are exposed to the wrong conditions, however, there is a slight chance of them catching fire or exploding.
At what temperature do lithium batteries explode?
Typically, lithium ion batteries operate at high temperatures but prolonged exposure to heat can damage the battery. The temperature at which a lithium ion battery explodes is 1000°F which is 538°C.


Comments are closed.